In the realm of mental health treatment, especially regarding eating disorders such as bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder, innovative approaches continue to emerge. Recent findings highlight the potential benefits of both web-based cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and pharmacological interventions involving glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). Together, these methods aim to not only address the psychological complexities of these conditions but also to offer tangible improvements in symptom management.
A recent study published in *JAMA Network Open* reveals promising data on the success of web-based CBT in mitigating symptoms of bulimia nervosa. Conducted by Steffen Hartmann and colleagues from Heidelberg University in Germany, this research examined the effectiveness of a structured online therapy module designed specifically for individuals battling bulimia. The study involved 154 adult participants, aged 19 to 65, who underwent either the web-based intervention or were assigned to a wait-list control group.
The results were noteworthy: participants engaging in the web-based CBT exhibited a significantly greater reduction in bulimic episodes compared to those who did not participate in the treatment. Although improvements in compensation behaviors—such as purging—were not significantly different between the two groups, the overall clinical results suggest the intervention may provide valuable support for individuals dealing with bulimia nervosa. The authors assert, “These findings underscore the effectiveness of web-based cognitive behavioral treatments for bulimia nervosa and suggest that these interventions can complement face-to-face therapies.” They also recommended further research into more extensive interventions that could yield better outcomes in addressing such behaviors and improving comorbid symptoms.
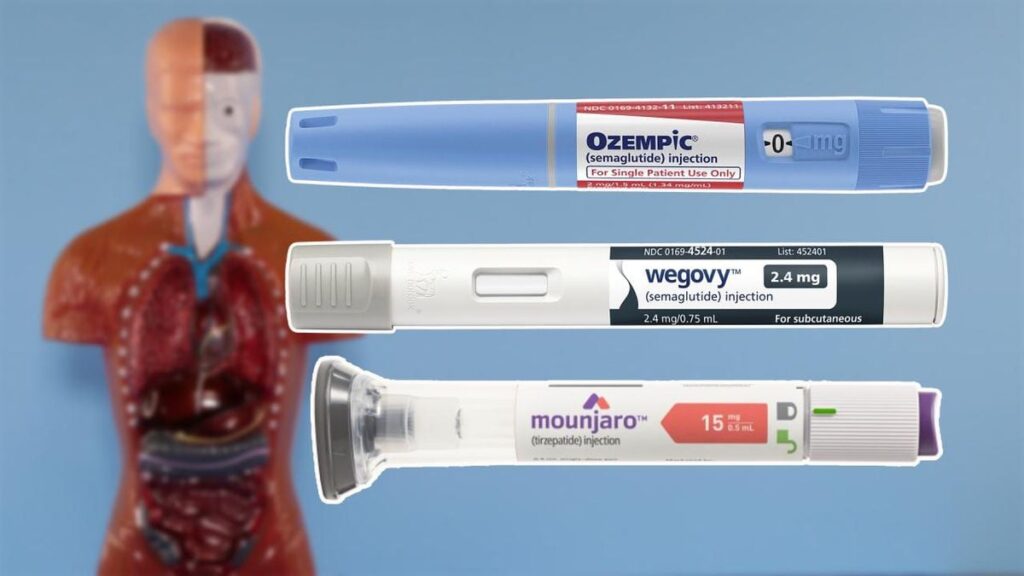
Shifting gears to the pharmacological landscape, new studies highlight the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists, historically used for managing type-2 diabetes and obesity, as novel treatments for binge eating and bulimia disorders. A systematic review conducted by scientists at Staten Island University Hospital indicated that GLP-1 RAs might be effective in reducing binge eating behaviors. The review suggests that these medications, by their nature, offer a dual advantage: they not only help with appetite control but also combat the emotional drive behind eating episodes.
GLP-1 itself is a hormone produced in the intestine and brain that plays a significant role in regulating appetite, decreasing food intake, and aiding in insulin secretion. Through their action on GLP-1 receptors, these drugs can effectively modulate feeding behaviors, making them a compelling option for eating disorder treatments. Current research findings, published in the *Journal of Clinical and Translational Endocrinology*, highlight the versatility of GLP-1 receptor agonists in managing not just eating patterns but also broader metabolic challenges associated with these disorders.
Both studies underscore a crucial understanding: tackling eating disorders requires multifaceted approaches. Traditional therapies, including psychological counseling and general dietary advice, often need to be supplemented with innovative treatments that could enhance recovery outcomes. The incorporation of technology through online therapies like CBT and the use of medication such as GLP-1 RAs represent significant progression in how healthcare providers can assist individuals struggling with these complex disorders.
As the research landscape evolves, further investigations into combinations of these treatments could pave the way for comprehensive care models. This could lead to integrated plans that address both psychological and physiological aspects of bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder, contributing to lowering the rates of these widespread conditions that affect millions globally.
In summary, promising advances in how we understand and treat these challenging eating disorders present hopeful prospects for those affected. As clinicians and researchers increasingly embrace hybrid models combining more traditional mechanisms with innovative approaches, the future looks brighter. Establishing effective treatment protocols that leverage the benefits of web-based CBT and GLP-1 medications may significantly enhance the lives of individuals grappling with the burdens of bulimia and binge eating.
The ability to access effective psychological therapies in a flexible online format could make treatment more appealing and accessible, particularly for those who may avoid in-person sessions due to stigma or anxiety. Additionally, the rising evidence supporting the pharmacological approach signifies a shift in the treatment paradigm, offering new avenues of hope and health for many.
As these therapeutic strategies continue to be explored, they hold the promise of creating a future where those dealing with these disorders not only find relief but also fully reclaim their lives from the grips of eating disorders.
Give Feedback. How was this article?
You can help us improve by leaving feedback specific to
this content.
Which of the following feelings did this article evoke in
you?
Multiple Selection
How would you rate the quality of this article?
How easy was it for you to find the information you were
looking for in this article?
Super Hard😱
😎Super Easy
Artificial intelligence is increasingly used in content
creation. What percentage of this article do you estimate was generated by AI?
How can we improve this article (or our articles in
general)?
Do you have any other suggestions for improving our content
or
website?
Thanks for the feedback
Thank you for supporting us to improve ourselves with your
feedback.